python data models performance
on this page
Overview
three approaches to data modeling in python:
- dataclasses: standard library data containers
- pydantic: validation and serialization
- sqlalchemy: database orm
this benchmark measures their relative performance.
Test Setup
each library implements the same model:
# Dataclass
@dataclass
class PersonDataclass:
name: str
age: int
email: str
active: bool = True
# Pydantic
class PersonPydantic(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
email: str
active: bool = True
# SQLAlchemy (with in-memory SQLite)
class PersonSQLAlchemy(Base):
__tablename__ = 'persons'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String)
age = Column(Integer)
email = Column(String)
active = Column(Boolean, default=True)Operations Tested
- creation: instantiating objects
- modification: updating attributes
- serialization: converting to dictionaries
10,000 iterations per operation, measured with time.perf_counter()
Results
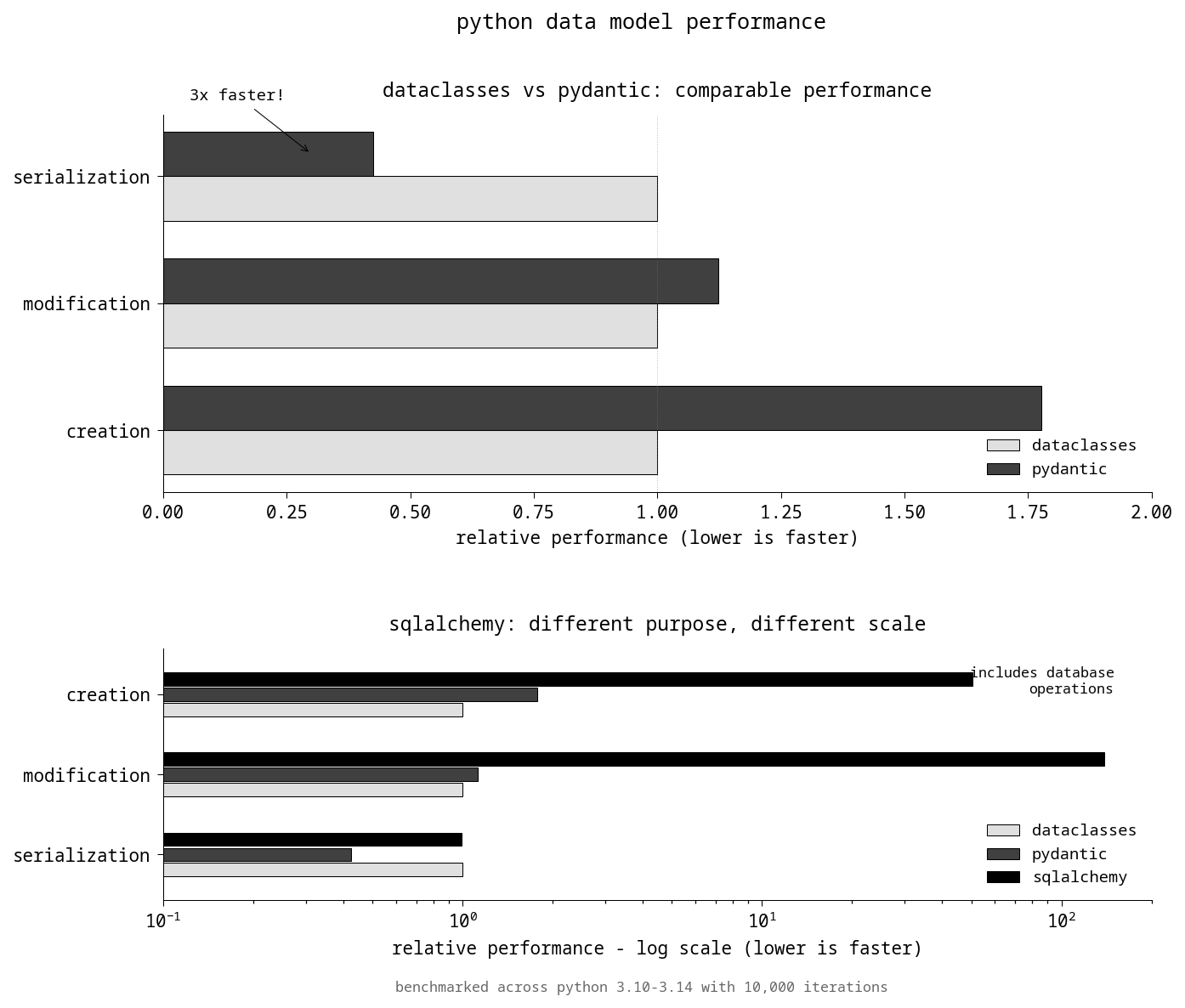
Average Performance (Python 3.10-3.14)
| library | creation | modification | serialization |
|---|---|---|---|
| dataclasses | 1.0x | 1.0x | 1.0x |
| pydantic | 1.8x slower | 1.1x slower | 2.5x faster |
| sqlalchemy | 50.5x slower | 138.8x slower | 1.0x |
Key Findings
- pydantic serializes ~2.5x faster due to rust-based implementation
- sqlalchemy operates at a different scale (50-140x slower) due to database operations
- dataclasses and pydantic have similar performance for basic operations
Actual Times (Microseconds)
| operation | dataclasses | pydantic | sqlalchemy |
|---|---|---|---|
| creation | 0.64 | 0.90 | 26.08 |
| modification | 1.72 | 1.96 | 239.49 |
| serialization | 2.78 | 0.76 | 2.03 |
When to Use Each
Dataclasses
- simple data containers
- validation not required
- zero dependencies
- significant performance improvements in python 3.13+
Pydantic
- data validation required
- json serialization workflows
- api development (fastapi)
- configuration management
SQLAlchemy
- database persistence
- complex queries and relationships
- transaction management
- database-agnostic applications
Benchmark Files
benchmark.py- benchmark runneranalyze.py- data analysisvisualize.py- visualizationsummary.json- aggregated resultsresults_python_*.json- raw data per python version
Running the Benchmarks
# Run benchmarks with specific Python version
uv run --python 3.14 --prerelease allow --with pydantic --with sqlalchemy python benchmark.py
# Analyze results
uv run --with matplotlib python analyze.py
# Generate visualizations
uv run --with matplotlib python visualize.pyConclusion
performance is one factor among many:
- dataclasses: optimal for simple use cases, especially with python 3.13+
- pydantic: best choice for validation and serialization workflows
- sqlalchemy: necessary for database-backed applications
choose based on requirements, not benchmarks alone.